Understanding Datatypes in JavaScript - Primitive and Non-Primitive
Javascript
Different Datatypes in Javascript
JavaScript is a most used programming language that uses different datatypes to deal with various kinds of information.
So what is Datatype?
In the world of programming, a datatype is a classification that specifies which type of value a variable can hold. It helps define the nature of the data and dictates the operations that can be performed on it. Think of datatypes as the building blocks that structure the information within your code
Which datatypes are there in Javascript?
a. Number:
- Represents numeric values, covering both integers and floating-point numbers.
- Size: 8 bytes.
- Example:
let num = 42;
b. String:
- Represents textual data, like words or sentences.
- Size: Variable.
- Example:
let text = "Hello, World!";
c. Boolean:
- Represents a binary choice - either
trueorfalse. - Size: 1 byte.
- Example:
let isTrue = true;
d. Null:
- Represents the deliberate absence of any object value.
- Size: N/A.
- Example:
let data = null;
e. Undefined:
- Represents an uninitialized variable.
- Size: N/A.
- Example:
let undefinedVar;
f. Symbol:
- Introduced in ECMAScript 6, it represents unique values.
- Size: Variable.
- Example:
let sym = Symbol("example");
g. Object:
- Represents a collection of key-value pairs.
- Size: Variable.
- Example:
let person = { name: "John", age: 30 };
h. Array:
- Represents an ordered list of values.
- Size: Variable.
- Example:
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
Example code of the different datatypes
// Number: Represents any kind of number
let age = 25;
let pi = 3.14;
// String: Represents text
let greeting = "Hello, World!";
let name = 'John';
// Boolean: Represents a simple choice (true or false)
let isCodingFun = true;
let isRainyDay = false;
// Null: Represents the absence of any information
let noData = null;
// Undefined: Represents a variable that hasn't been given a value yet
let notDefined;
// Symbol: Represents a unique identifier
let uniqueKey = Symbol("example");
// Object: Represents a bunch of information organized in pairs
let person = {
name: "Alice",
age: 30,
isStudent: true
};
// Array: Represents a list of information
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let fruits = ['apple', 'orange', 'banana'];
// Using typeof to identify datatypes
console.log(typeof age); // Outputs: number
console.log(typeof greeting); // Outputs: string
console.log(typeof isCodingFun); // Outputs: boolean
console.log(typeof noData); // Outputs: object (Note: typeof null is an interesting quirk in JavaScript)
console.log(typeof notDefined); // Outputs: undefined
console.log(typeof uniqueKey); // Outputs: symbol
console.log(typeof person); // Outputs: object
console.log(typeof numbers); // Outputs: object (Arrays are also objects in JavaScript)
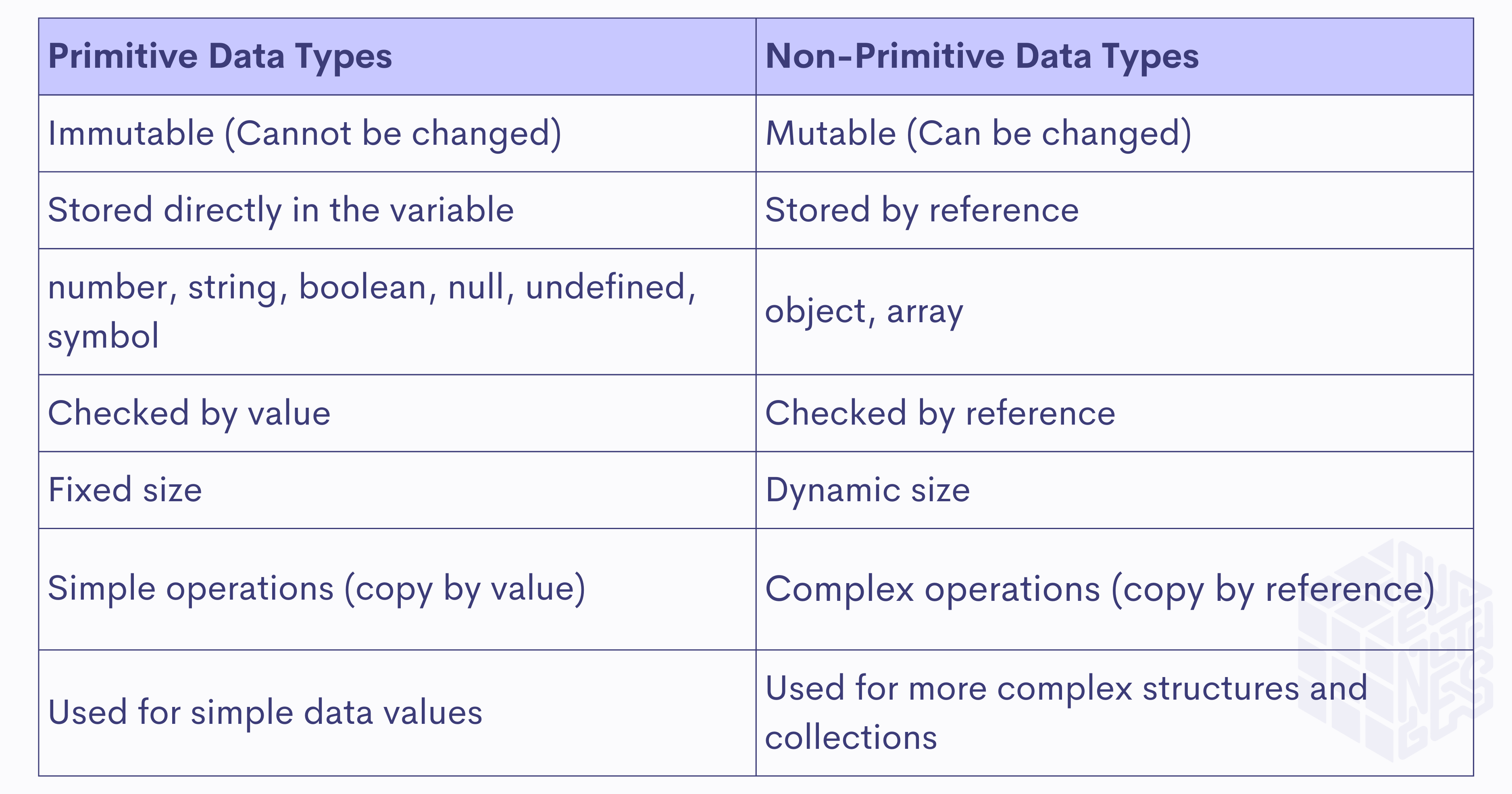
What is Primitive and Non-Primitive Data Type?
In JavaScript, datatypes are classified as either primitive or non-primitive. Primitive types are fundamental and immutable, while non-primitive types are more complex and mutable.
List of Primitive Datatypes
- Number
- String
- Boolean
- Null
- Undefined
- Symbol
List of Non-primitive Datatypes
- Object
- Array
How to Find Type in JS?
Determining the type of a value in JavaScript is crucial. The typeof operator can be used for this purpose.
For Example:
let exampleValue = "Hello, World!";
console.log(typeof exampleValue);
// Outputs: string
More Insights about Datatypes in JS:
Beyond the core questions, let’s consider additional aspects that deepen our understanding of JavaScript datatypes:
- Data Conversion: JavaScript allows implicit and explicit data type conversion. Knowing when and how to convert data types is essential for efficient code.
- Type Coercion: It means when different types of data are used in one operation, the code automatically converts the data according to the preferred datatype. JS can performs type coercion during operations involving different datatypes.
Wrapping It Up,
JavaScript datatypes might seem a bit complex at first, but they’re like tools in your coding toolbox. The more you understand them, the more powerful you become as a coder.
This is just the beginning of the journey into JavaScript datatypes. Feel free to explore further and discover how these tools can make your coding adventures even more exciting!
